Initial details of the first HPEV (high performance electrified vehicle) hybrid super sports car from Lamborghini have been unveiled. Codenamed LB744, the vehicle is scheduled to make its debut in 2023.
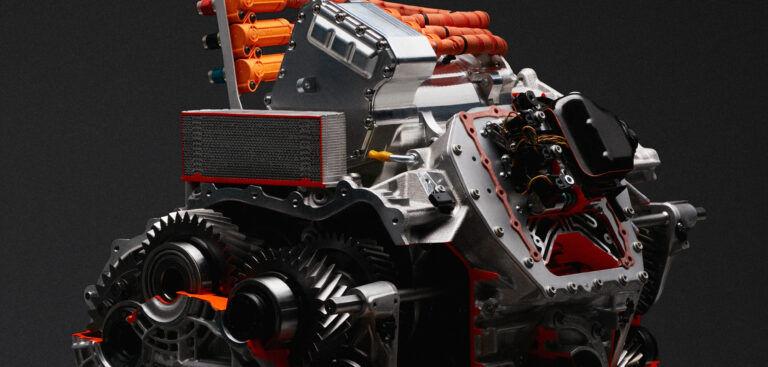
The LB744 uses an all-new architecture combined with a new powertrain to deliver more than 1,000ps in total through a combination of a brand-new 12-cylinder internal combustion engine and three electric motors. A double clutch gearbox also makes its debut on the model.
For the powertrain, Lamborghini has chosen to use a naturally aspirated 6.5-liter V12 mid-mounted engine, aided by three electric motors, with one integrated into the double-clutch 8-speed gearbox. For the first time, this is mounted transversely and placed behind the combustion engine. The transmission tunnel has now been repurposed and houses a 3.8kWh lithium-ion battery to power the electric motors. If required, the LB744 can be used as a purely electric car, reducing overall CO2 emissions by 30% compared to the Lamborghini Aventador Ultimae.
The new engine, coded the L545, is the lightest and most powerful 12-cylinder engine ever made by the Italian vehicle manufacturer, weighing just 218kg. The superquadro V12 has a maximum power output of 825ps at 9,250rpm, made possible through a redesigned distribution system which supports 9,500rpm. Maximum torque is 725Nm at 6,750rpm. Other redesigned components include the air intake ducts which now draw in an increased amount of airflow. Combustion within the engine has also been optimized due to the regulation of ionization in the chamber with two control units. A 12.6:1 compression ratio features.
 As with previous Lamborghini models, the LB744 benefits from a four-wheel drive system, with the ICE providing power to the rear wheels while a pair of electric motors supplies power to each of the front wheels. A third electric motor situated above the gearbox can also supply power to the rear wheels, depending on the selected driving mode.
As with previous Lamborghini models, the LB744 benefits from a four-wheel drive system, with the ICE providing power to the rear wheels while a pair of electric motors supplies power to each of the front wheels. A third electric motor situated above the gearbox can also supply power to the rear wheels, depending on the selected driving mode.
Each electric motor can deliver 350Nm and features a torque vectoring function to optimize driving dynamics. The components can also be used for recuperating energy produced under braking.
Lamborghini has developed a new compact transmission unit which was designed entirely in-house and, after the LB744, it will be used within Lamborghini’s next generation of super sports cars.
A wet double clutch was chosen as the most efficient and performance-oriented solution for the LB744, capable of handling the high torque figures from the internal combustion engine. Inside the newly developed gearbox are two distinct shafts as opposed to the normal three. One is responsible for the even-numbered gears, and the other the odd gears. Both engage the same rotor, reducing overall weight and saving space. Compared to the 7-speed double clutch unit in the Huracán, the LB744’s gearbox is faster in terms of shifting speed.
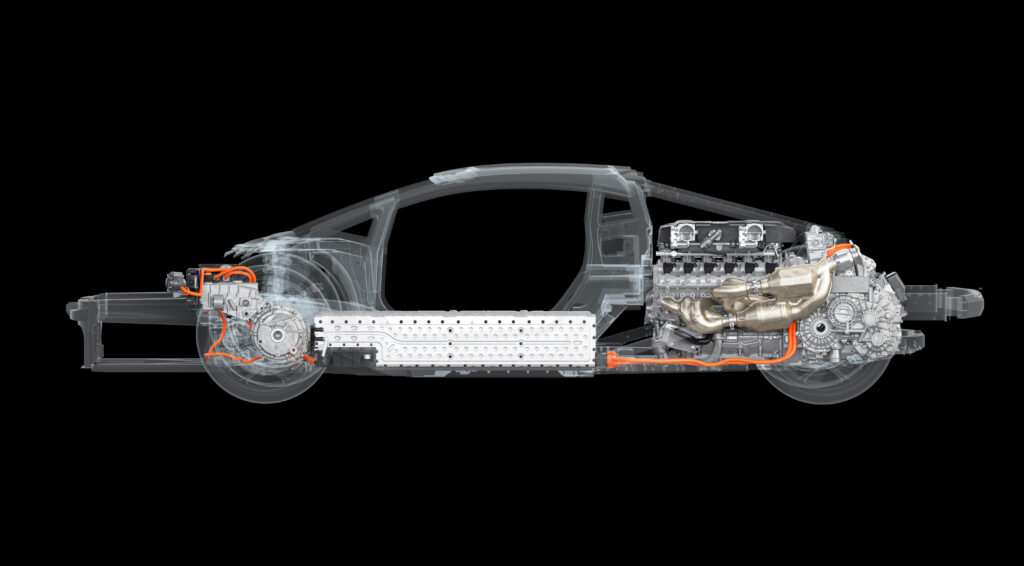 Situated above the gearbox is the rear electric motor, with a maximum power of 110kW and a peak torque of 150Nm. Working as both the starter motor and generator, the rear electric motor also supplies energy to the front electric motors via the battery in the transmission tunnel. In full electric mode, the motor provides power to the rear wheels that, while the e-motors at the front drive the front wheels, enabling zero-emission four-wheel drive.
Situated above the gearbox is the rear electric motor, with a maximum power of 110kW and a peak torque of 150Nm. Working as both the starter motor and generator, the rear electric motor also supplies energy to the front electric motors via the battery in the transmission tunnel. In full electric mode, the motor provides power to the rear wheels that, while the e-motors at the front drive the front wheels, enabling zero-emission four-wheel drive.
Depending on the selected driving mode, an uncoupling mechanism is used with a dedicated synchronizer to enable a connection to the double-clutch gearbox. When it is providing additional power to the V12 engine, the electric motor is in the P3 position, separated from the gearbox. It can then move into the P2 position to recharge the battery at low speeds.
Click here for more on hybrid powertrain technologies.