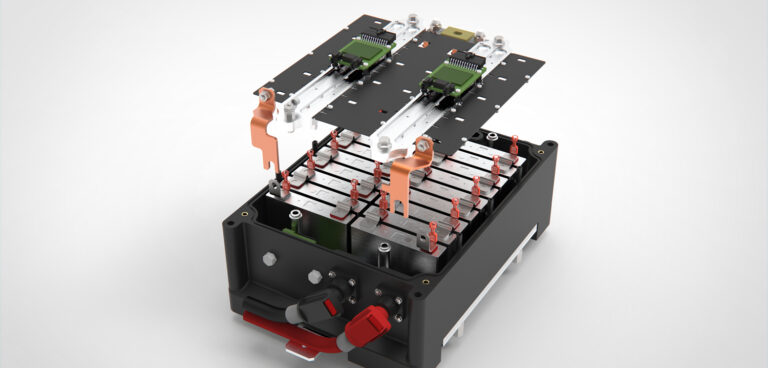
Mahle Powertrain has detailed developments of its new 48V battery design, showcasing the potential performance benefits that the technology can offer. The engineering services company has designed and developed a working prototype battery.
“The draw of a 48V system is that it offers similar fuel economy benefits to high-voltage systems, but at a much lower cost. However, we quickly saw that the architecture is inherently limited by battery module compromises necessitated by cost and packaging constraints,” explained Mike Bassett, Mahle Powertrain’s chief engineer for research and advanced engineering (below right).
 “We have carried out extensive studies into the requirements of a 48V system to establish an optimal balance of the powertrain components, and our analysis has identified a pathway to develop an MHEV that is able to provide CO₂ benefits of 12-15%.”
“We have carried out extensive studies into the requirements of a 48V system to establish an optimal balance of the powertrain components, and our analysis has identified a pathway to develop an MHEV that is able to provide CO₂ benefits of 12-15%.”
Mild hybrids need to recover energy efficiently and at a high rate during deceleration. However, packaging and cost factors encourage the use of more compact batteries with reduced storage capacity. This means that OEMs require a small battery pack that is capable of high-power charge and discharge cycles.
“We revisited the very question, ‘What is needed from a 48V vehicle?’ to minimize any limitations and to demonstrate the attainability of an enhanced powertrain solution,” added Bassett. “We based our analysis on our existing C-segment 48V demonstrator.”
The demonstrator is fitted with a 1.2-liter, turbocharged three-cylinder engine equipped with a belt-integrated starter generator (BSG) and 48V electric supercharger. The vehicle already provides performance akin to the production 2-liter TGDi equivalent, with CO₂ figures 12% lower over the WLTP test procedure. This is expected to improve further when fitted with Mahle Powertrain’s new 48V high power battery and an equally capable 48V e-axle.
“Setting the right high-level performance targets was crucial, as it enabled the appropriate selection of cells for our battery pack development,” says Bassett. “Balance is key: matching the total mass of cells needed with packaging requirements and pack performance targets enables the development of a pack with high power capability and relatively low energy storage capacity.”
 Inadequate battery cooling can have a significant impact on charge and discharge performance and battery life. Bassett said the difficulty was the narrow difference between battery and ambient temperatures: “We wanted to replace traditional air-cooling with a liquid coolant, which could then potentially be linked to the vehicle air-conditioning system in hot climates, but of course we needed to overcome the challenge of keeping coolant electrically separate from the cells.”
Inadequate battery cooling can have a significant impact on charge and discharge performance and battery life. Bassett said the difficulty was the narrow difference between battery and ambient temperatures: “We wanted to replace traditional air-cooling with a liquid coolant, which could then potentially be linked to the vehicle air-conditioning system in hot climates, but of course we needed to overcome the challenge of keeping coolant electrically separate from the cells.”
Mahle engineers also focused on circuit and bus bar design and materials to minimize the chances of short-circuit. Basset explained, “Even though 48V is technically a safe system when compared to much larger 350-400V battery packs, short circuits can still release considerable energy, and we wanted to maximize the reliability of the system as well as its performance.”
The new design will enable better energy recovery and a faster charge, which boosts efficiency. Bassett emphasized that a higher power capable battery pack creates tangible efficiency benefits on the road, offering a 12% fuel saving over the new WLTP standards, assuming ICE efficiency remains constant.